 CacheGuard-OS
CacheGuard-OSUser's Guide - Version UF-2.5.1
Web Authentication
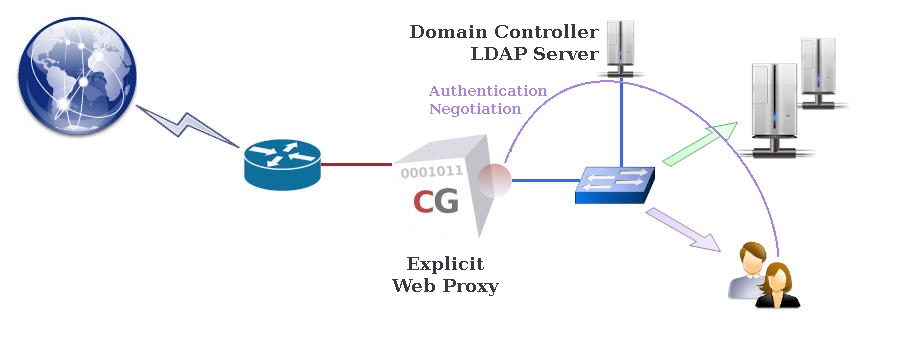
Web authentication can be used in conjunction with the web and rweb modes to restrict Web browsing and/or access to reverse websites to authenticated users only. By activating Web authentication mode, explicit users of the Web proxy in forwarding/browsing mode (web mode) and/or external users of reverse websites in reverse mode (rweb mode) are required to authenticate before being allowed to connect to the CacheGuard appliance. The CacheGuard appliance supports LDAP and Kerberos authentication modes, which you can configure using the authenticate command.LDAP Authentication
In LDAP authentication mode, the first time a Web user tries to access a Web page, they are asked to submit their credentials via a pop-up window opened by the Web browser. With this authentication method, called basic authentication, the CacheGuard appliance submits the collected credentials to an LDAP server. If the submitted credentials are validated by the LDAP server, the CacheGuard appliance allows the Web user to connect. Otherwise, their access request is rejected. You can activate Web authentication by using the mode authenticate on command.To configure LDAP authentication, you must specify at least one LDAP server and the LDAP request that should be sent to it to authenticate users. In addition, as most LDAP servers require clients to bind before accepting requests, you must configure the LDAP binding in your authentication settings. For example, the commands below configure LDAP authentication to send the 'ou=people,dc=example,dc=com' 'uid' 'userPassword' 'objectClass=inetOrgPerson' request to the LDAP server with the ldap.example.com 10.0.10.201 hostname and IP address. As this LDAP server requires binding, the LDAP binding is activated by specifying the 'cn=admin,dc=example,dc=com' bind DN (Distinguished Name).
- mode authenticate on
- authenticate web on
- authenticate mode ldap on
- authenticate ldap request 'ou=people,dc=example,dc=com' 'uid' 'userPassword' 'objectClass=inetOrgPerson'
- authenticate ldap server add ldaps ldap.example.com 10.0.10.201
- authenticate ldap binddn 'cn=admin,dc=example,dc=com' on
- apply
Please note that if an empty value ('') is specified as the password LDAP attribute, an LDAP binding is performed during the basic authentication phase instead of comparing the entered password with the value stored in the password LDAP attribute (this is the preferred method used by Microsoft® AD). If your LDAP server is a Microsoft® AD, you can use the following commands to configure LDAP authentication:
- mode authenticate on
- authenticate mode ldap on
- authenticate ldap request 'cn=users,dc=example,dc=com' 'sAMAccountName'
- authenticate ldap server add ldaps ldap.example.com 10.0.10.201
- authenticate ldap binddn 'cn=webgateway,cn=users,dc=example,dc=com' on
- apply
Kerberos Authentication
In Kerberos authentication mode, the credentials used by users to log in to their workstations are retrieved by the CacheGuard appliance during a negotiation phase and then used to authenticate Web users. Kerberos-based authentication is a complex process that goes beyond this documentation, so we will focus on how to configure the CacheGuard appliance to use Microsoft® AD (as a Kerberos server).
- mode authenticate on
- authenticate mode ldap off
- authenticate mode kerberos on
- authenticate kerberos web proxy
- authenticate ad rdn 'cn=computers'
- domainname example.com
- authenticate kerberos server add dc.example.com
- authenticate kerberos encrypt aes
- apply
It is IMPORTANT to note that the first time Kerberos authentication mode is activated (after the apply operation completes), it must be initialised on the CacheGuard appliance. During the initialisation process, if the LDAP object representing the Web proxy in Microsoft® AD does not yet exist, a new LDAP object for that Web proxy is created in Microsoft® AD. The initialisation process allows the CacheGuard appliance to obtain a Kerberos ticket. To initialise Kerberos authentication, use the authenticate kerberos create administrator command. This command requires you to enter interactively the password associated with the used administrator account. The entered password is not permanently saved and is removed after obtaining the Kerberos ticket. Please note that the Microsoft® AD account used should have administrator permissions (for instance, the administrator user). The Kerberos initialisation is an asynchronous operation executed in the background. The authenticate kerberos report command allows you to display a report on the Kerberos initialisation process.